gvSIG-Desktop 1.10. User Manual
Once the inputs have been defined, it is time to define the algorithms to apply on them. Algorithms can be found in the Processes tab, grouped much in the same way as they are in the toolbox.
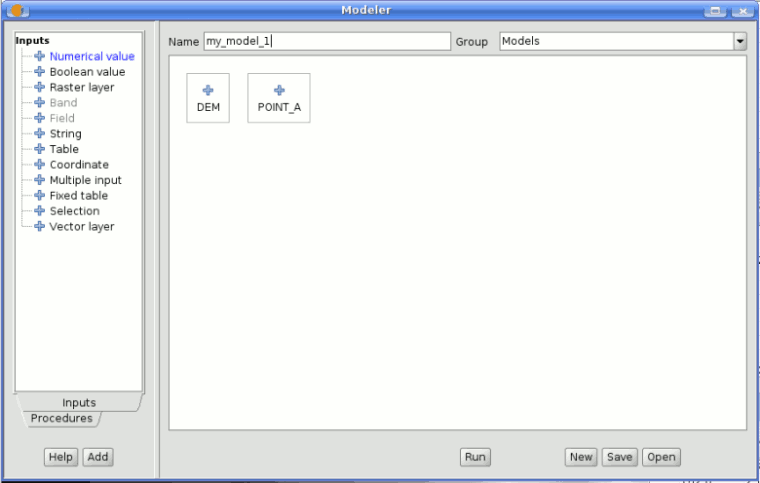
SEXTANTE modeler
To add a process, double-click on its name. An execution dialog will appear, with a content similar to the one found execution panel that SEXTANTE shows when executing the algorithm from the toolbox.
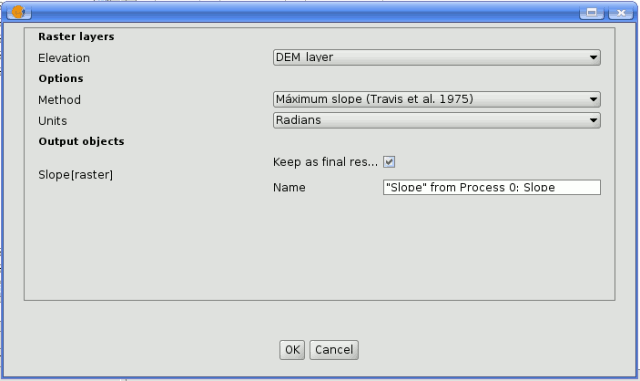
SEXTANTE modeler process
Some differences exist, however, the main one being the absence of a raster ouput tab, even if the selected algorithm generates raster layers as output.
Instead of the textbox that was used to set the filepath for output layers and tables, a checkbox and a text box are found. If the layer generated by the algorithm is just a temporary result that will be used as the input of another algorithm and should not be kept as a final result, the check box should be left unchecked. Checking it means that the result is a final one, and you have to supply also a valid description for the output, which will be the one the user will see when executing the model.
Selecting the value of each parameter is also a bit different, since there are important differences between the context of the modeler and the toolbox one. Let's see how to introduce the values for each type of parameter.
- Layers (raster and vector) and tables. They are selected from a list, but in this case the possible values are not the layers or tables currently loaded in the GIS, but the list of model input or the corresponding type, or other layers or tables generated by algorithms already added to the model.
- Numerical values. Literal values can be introduced directly on the textbox. This textbox is a list that can be used to select any of the numerical value input of the model. In this case, the parameter will take the value introduced by the user when executing the model.
- String. Like in the case of numerical values, literal strings can be typed, or an input string can be selected
- Points. Coordinates cannot be directly introduced. Use the list to select one of the coordinate inputs of the model
- Bands. The number of bands of the parent layer cannot be known at designtime, so it is not possible to show the list of available bands. Instead, a list with band numbers from 1 to 250, as well as the band parameters of the model, is shown. At runtime, SEXTANTE will check if the parent raster layer selected by the user has enough bands and the given band has therefore a valid value, and if not it will generate an error message.
- Table field. Like in the previous case, the elds of the parent table or layer cannot be known at designtime, since they depend of the selection of the user each time the model is executed. To set the value for this parameter, type the name of a field directly in the textbox, or use the list to select a table field input already added to the model. The validity of the selected field will be checked by SEXTANTE at runtime
- Selection. The list contains in this case not only the available option from the algorithm, but also the selection inputs already added to the current model
Once all the parameter have been assigned valid values, click on OK and the algorithm will be added to the canvas. It will be linked to all the other elements in the canvas, whether algorithms or inputs, which provide objects that are used as inputs for that algorithm.

SEXTANTE model









